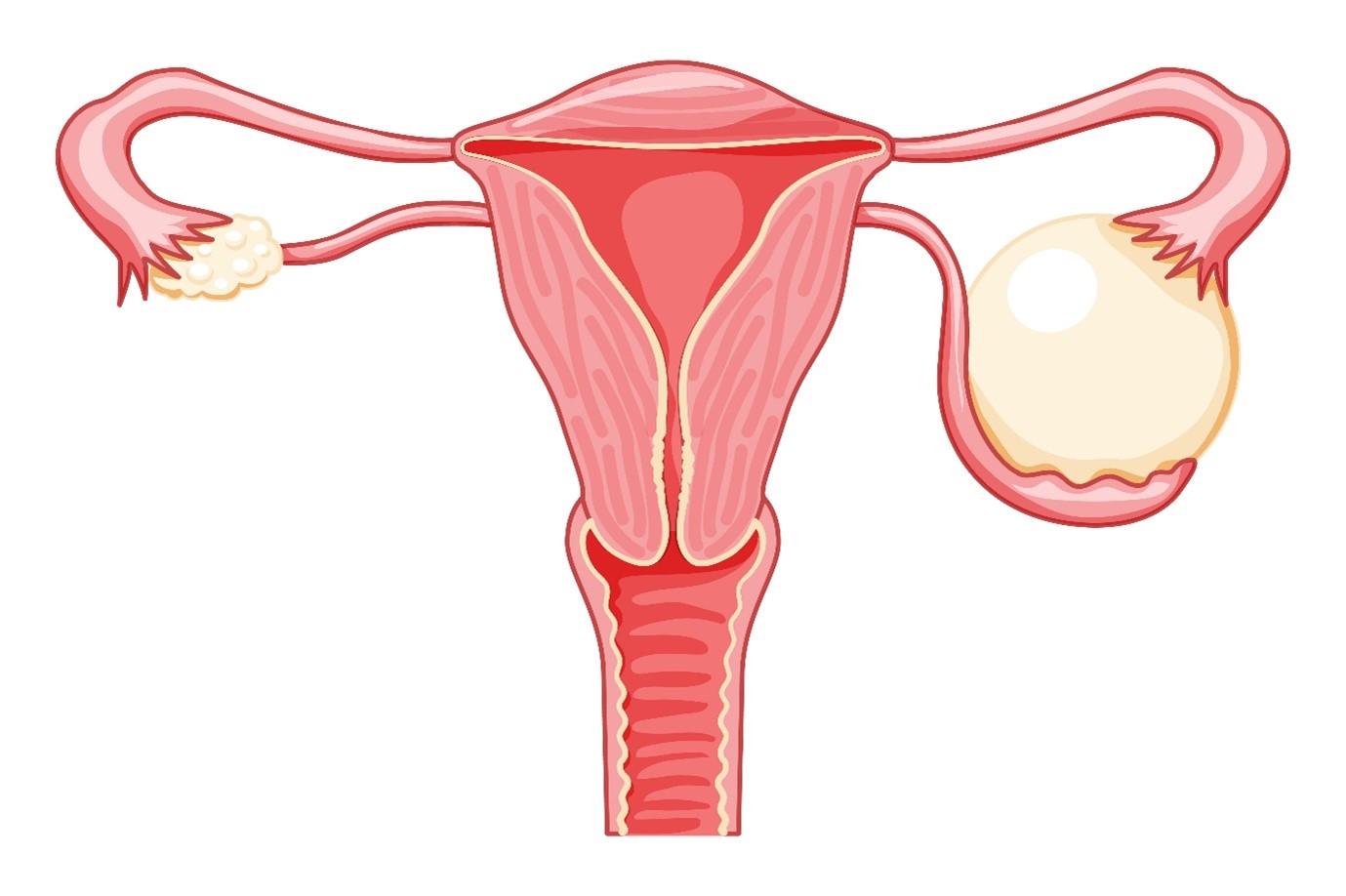
What is an Ovarian Cyst
It is a sac filled with fluid that develops on or inside one or both ovaries. These cysts are incredibly common and usually non-cancerous (benign). In fact, many ovarian cysts are harmless and go unnoticed, only discovered during routine pelvic exams or ultrasounds. Ovarian cysts often shrink naturally without the need for treatment. Most of the time, ovarian cysts shrink on their own and do not require treatment. However, some cysts can cause complications or pain. Regular check-ups and screenings are important in ensuring that any cysts are monitored, especially when they cause discomfort or when they appear after menopause.
What Are the Different Types of Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are categorized into different types based on their formation, contents, and associated conditions. Here are the most common types:
Functional Cysts: These are the most common type and are directly related to the menstrual cycle. They are typically benign and include:
Follicular Cysts: These form when the follicle, which is supposed to release an egg during ovulation, fails to do so. Instead, the follicle fills with fluid and forms a cyst.
Corpus Luteum Cysts: After ovulation, the follicle transforms into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces hormones. Sometimes, the corpus luteum doesn't dissolve as expected and fills with fluid, creating a cyst.
Other Types of Cysts:
Cystadenomas: These cysts develop on the ovary's surface and can be filled with either a watery fluid or a thicker, mucus-like substance.
Dermoid Cysts: Dermoid cysts contain tissue similar to skin, hair, or even teeth. These cysts are typically benign and are usually present from birth.
Endometriomas: These cysts are linked to endometriosis and are filled with old menstrual blood. They occur when tissue from the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, affecting the ovaries.
Ovarian Cancer Cysts: Though rare, ovarian cancer can form cysts that are solid and cancerous, typically in women after menopause.
Although most ovarian cysts are benign, some may grow large, cause pain, or lead to complications. Monitoring these cysts is crucial, especially after menopause when the risk of malignancy increases.
What Causes Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are primarily caused by the process of ovulation, but they can also arise due to other health conditions or disruptions in normal cell growth. The common causes of ovarian cysts include:
Ovulation: The most common cause of ovarian cysts, where functional cysts form as part of the menstrual cycle. They typically resolve on their own within a few months.
Abnormal Cell Growth: Abnormal cell reproduction can cause cysts like dermoid cysts or cystadenomas.
Endometriosis:
In cases of endometriosis, tissue resembling the uterine lining grows outside the uterus and can develop into cysts called endometriomas.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder resultng in the formation of multiple cysts on the ovaries.
Pelvic Infections (PID): Infections in the pelvic area can spread to the ovaries and cause cysts.
Additionally, the likelihood of developing ovarian cysts increases with factors such as age (particularly before menopause), pregnancy status, and a history of previous cysts. Conditions like endometriosis and PCOS can also increase the chances of cyst formation.
What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts often cause no symptoms and can go unnoticed, especially when they are small. However, larger cysts or cysts that develop due to conditions like endometriosis or PCOS may cause the following symptoms:
Pelvic Pain: A mild ache or intense pain, usually on one side of the lower abdomen.
Bloating or Fullness: A feeling of pressure or fullness in the abdomen, sometimes on one side.
Pain During Intercourse: Pain or discomort during or after sexual activity.
Irregular or Painful Periods: This may include changes in menstrual cycles or intense period cramps.
Digestive Issues: Difficulty passing stools, feeling full after eating small amounts, or frequent urination.
In some cases, symptoms may indicate more serious conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can also cause hormonal imbalances, acne, weight gain, and infertility.
What Are the Treatment and Management Options for Ovarian Cysts?
The treatment for ovarian cysts depends on the type of cyst, its size, whether it causes symptoms, and your health history. Here are the common treatment options:
Watchful Waiting: For functional cysts that are small and asymptomatic, a "wait and see" approach may be recommended. These cysts often shrink on their own within a few months. Regular follow-up ultrasounds are used to monitor changes.
Medications: Hormonal birth control pills may be prescribed to regulate ovulation and prevent future cysts from forming. This is more common for women with recurrent cysts or those with conditions like PCOS.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be needed to remove the cyst, especially if it’s large, causing symptoms, or suspected to be cancerous. The two main types of surgery are:
Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure that involves small incisions through which the cyst is removed. It generally offers a quicker recovery time.
Laparotomy: A more invasive surgery that requires a larger incision and is performed when the cyst is large or there are other concerns.
If the cyst is suspected to be cancerous, further testing and consultation with a gynecological oncologist may be necessary for comprehensive treatment options.
When Should You Seek Medical Help?
While most ovarian cysts are harmless, you should consult your healthcare provider if you experience the following symptoms, which may indicate complications:
Persistent Pelvic Pain: Pain that doesn't go away or worsens over time.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Changes in the frequency or intensity of your periods.
Pain During Intercourse: Unexplained pain during or after sexual activity.
Severe Symptoms of a Ruptured Cyst: This includes sudden sharp pain, nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness, or fainting.
Abdominal Swelling or Bloating: A noticeable increase in abdominal size or discomfort.
These symptoms could indicate serious complications such as ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary) or cyst rupture, both of which require immediate medical attention.
Why Choose Pankajam Memorial Hospital for Your Ovarian Cyst Care?
At Pankajam Memorial Hospital, we offer comprehensive gynecological care, ensuring the well-being of women through advanced diagnostics and treatments. Whether you're in need of routine screenings, cyst monitoring, or specialized care, our team of experienced healthcare professionals is here to help.
Our state-of-the-art facilities include:
Pelvic Ultrasound: To accurately detect and monitor ovarian cysts.
Laparoscopic Surgery: For minimally invasive removal of cysts.
Personalized Care: Each treatment plan is tailored to your individual needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
We prioritize your health and are committed to providing effective solutions for all types of ovarian cysts. Whether you need help understanding your condition, managing symptoms, or undergoing surgery, Pankajam Memorial Hospital is your trusted partner in healthcare.
Book Your Consultation Today!
Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen—early detection and treatment of ovarian cysts can prevent complications and help you maintain optimal health. Contact Pankajam Memorial Hospital today to book your consultation and take the first step toward a healthier, pain-free future. Our compassionate team is here to support you every step of the way!