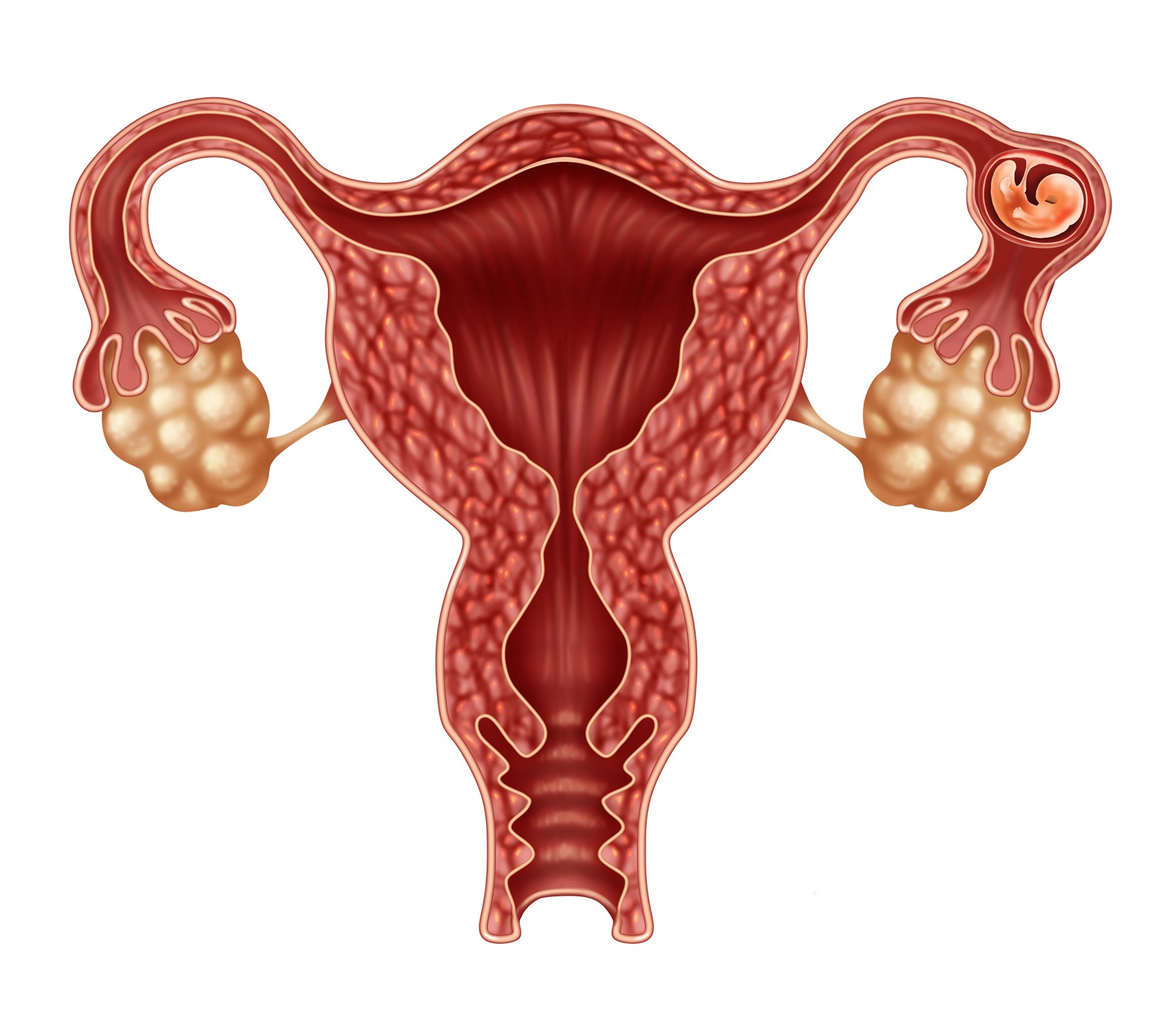
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, with the fallopian tube being the most common location for this to happen.
This situation prevents the pregnancy from developing correctly, as the uterus is the only organ capable of supporting a growing fetus.
If left untreated, an ectopic pregnancy can become life-threatening, particularly if the fallopian tube ruptures, leading to severe bleeding and requiring immediate medical intervention.
What Are the Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy?
Early symptoms of ectopic pregnancy can resemble those of a normal pregnancy but may also include:
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pain in the lower belly, pelvic region, or lower back.
- Dizziness or weakness
If the fallopian tube ruptures, symptoms can escalate to:
- Severe, sharp abdominal pain
- Fainting
- Low blood pressure
- Shoulder pain
- Rectal pressure
These signs may indicate a medical emergency, and immediate contact with a doctor or a visit to the emergency room is crucial.
What Causes Ectopic Pregnancy?
Multiple factors can elevate the risk of an ectopic pregnancy, typically associated with conditions that obstruct the movement of the fertilized egg along the fallopian tube.
These factors include:
- Previous ectopic pregnancies
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Fallopian tube surgeries
- Infertility history
- Endometriosis
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Presence of an IUD
Age is also a contributing factor, with individuals over 35 having a higher risk.
Notably, up to 50% of those experiencing an ectopic pregnancy have no identifiable risk factors.
How is Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Ectopic pregnancies are typically diagnosed during early pregnancy care through several tests, including:
- Urine test: Checks for pregnancy.
- Blood test: Assesses the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) levels. Low levels may suggest an ectopic pregnancy.
- Ultrasound: Provides images of internal structures to locate the implantation site.
Sometimes, doctors may perform additional tests if a rupture is suspected.
How is Ectopic Pregnancy Treated?
Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy typically involve medication or surgery, depending on the situation:
- Medications: Some drugs are given as an injection to hinder the growth of the fertilized egg. It's most effective when there's no rupture.
- Surgery: If the fallopian tube has ruptured, emergency surgery is required. This can involve removing the entire tube or the egg, preserving the tube's function.
Recovery and future pregnancy plans should be discussed with your doctor after treatment.
If you suspect you are experiencing symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy or want more information, contact Pankajam Memorial Hospital today for expert guidance and care. Your health and peace of mind are our top priorities!